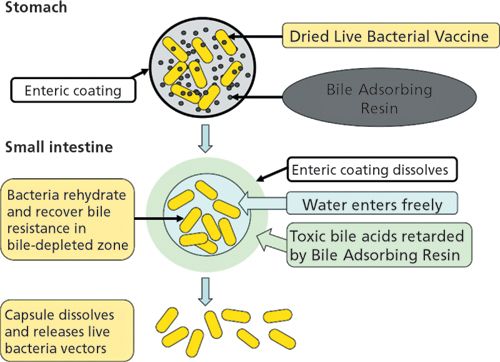
types of vaccine delivery system
Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine. This type of imitation infection helps teach the immune system how to.

All Types Of Covid 19 Vaccines How They Work Animation Youtube
Vaccine delivery systems are generally particulate eg.

. Updated bivalent booster counts include the number of people administered a vaccine dose with a Covid-19 vaccine code CVX code 229 Moderna. With the pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccine delivery systems emerged as a core technology for global public health. Vaccine-induced immune responses can be enhanced by mimicking the properties of pathogens.
An injectable vaccine may be delivered in either a 1-mL or 3-mL syringe as long as the prescribed dosage is delivered. Most vaccines require co-delivery of an adjuvant in order to generate the desired immune responses. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Live attenuated and live inactivated whole virus. This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the. Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles.
Vaccines can help protect against certain diseases by imitating an infection. Each vaccine exhibits a different potency and duration of efficacy as determined by the antigen design adjuvant molecules vaccine delivery platforms and immunization method. Needle Selection the needle should be suitable for the.
IC31 and IC30 novel types of vaccine adjuvant based on peptide delivery systems Expert Rev Vaccines. How Vaccines Work. This vaccine type can be split into two major types.
Authors Karen Lingnau 1. Given that antigen processing takes. However many currently available adjuvants are non-biodegradable have.
In sum modulating the administration distribution metabolism and excretion of a vaccine will greatly impact its in vivo fate. What are the components of vaccine delivery system. Liposomes and liposome-derived nanovesicles such as archaeosomes and virosomes have become important carrier systems in vaccine development and the interest for liposome.
Considering these factors in the design of a vaccine. Emulsions microparticles iscoms and liposomes and mainly. Inactivated viruses are more commonly used due to their inability to.
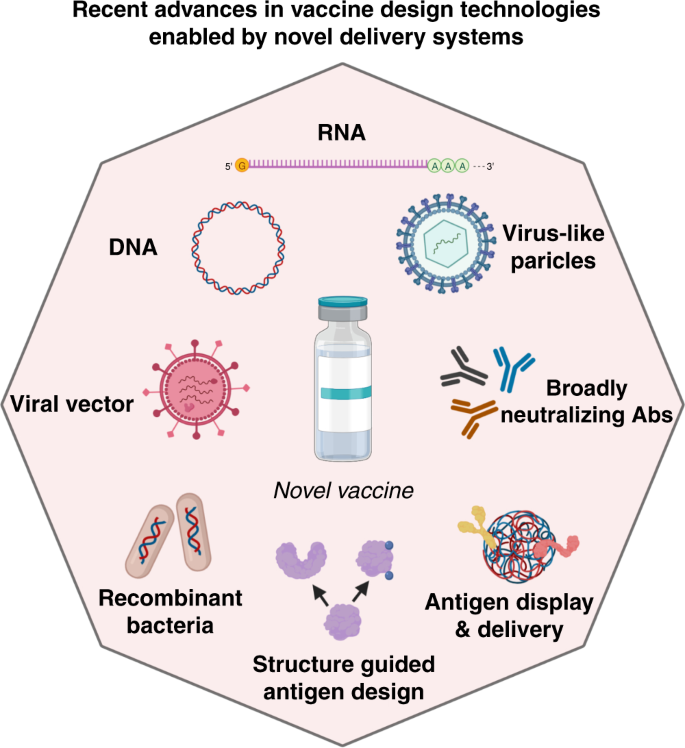
The Sixth Revolution In Pediatric Vaccinology Immunoengineering And Delivery Systems Pediatric Research

Vaccine Innovations Past And Future Nejm

Types Of Vaccine Vaccine Knowledge

An Alphavirus Derived Replicon Rna Vaccine Induces Sars Cov 2 Neutralizing Antibody And T Cell Responses In Mice And Nonhuman Primates Science Translational Medicine

Non Viral Covid 19 Vaccine Delivery Systems Sciencedirect

Us States Are Beginning The Work Of Vaccination Mckinsey

Novel Mucosal Vaccine Delivery Systems Download Scientific Diagram

States Are Getting Ready To Distribute Covid 19 Vaccines What Do Their Plans Tell Us So Far Kff

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
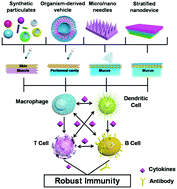
Up To Date Vaccine Delivery Systems Robust Immunity Elicited By Multifarious Nanomaterials Upon Administration Through Diverse Routes Biomaterials Science Rsc Publishing

Vaccine Definition Types History Facts Britannica

Liposomes Used As A Vaccine Adjuvant Delivery System From Basics To Clinical Immunization Sciencedirect

Why Global Vaccine Equity Is The Prescription For A Full Recovery
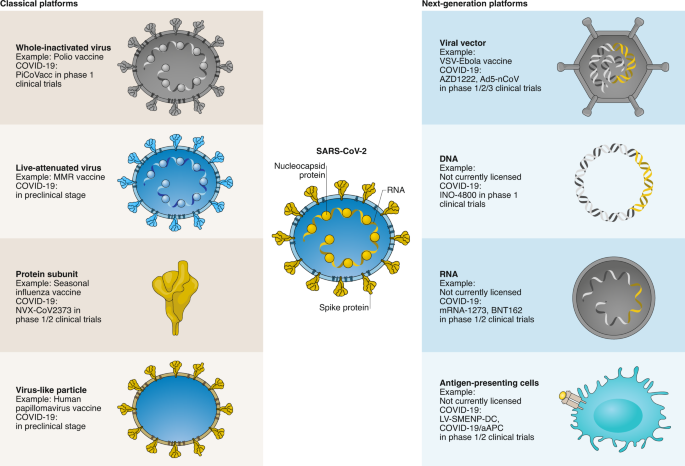
Next Generation Vaccine Platforms For Covid 19 Nature Materials

Polymers Strive For Accuracy From Sequence Defined Polymers To Mrna Vaccines Against Covid 19 And Polymers In Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Journal Of The American Chemical Society
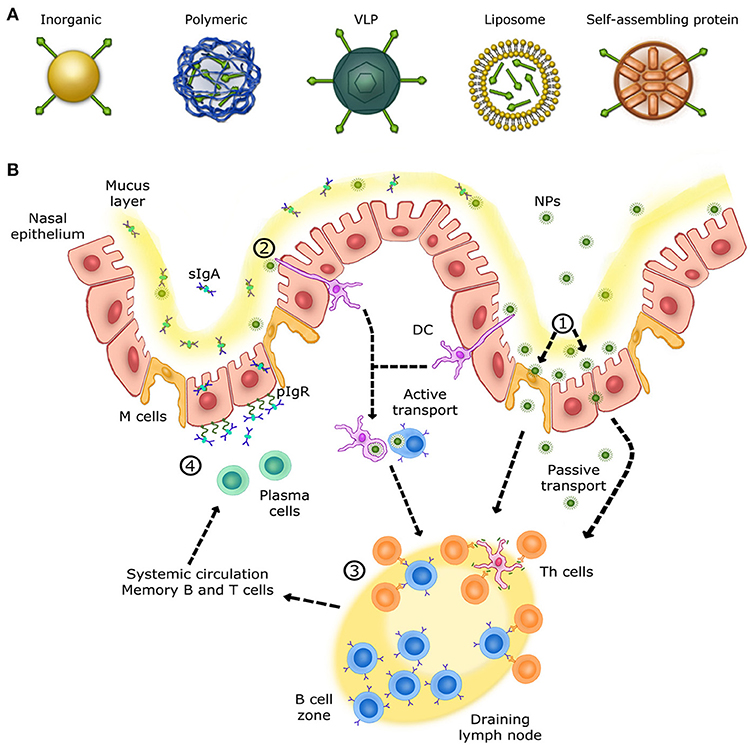
Frontiers Nanoparticle Based Vaccines Against Respiratory Viruses

How The Johnson Johnson Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times